
Knee pain is one of the most common symptoms for which patients turn to orthopedists and other specialists. Many people completely ignore the appearance of unpleasant sensations, considering them age-related and almost natural. But there are many prerequisites for pain in the knee joint, because it has a complex structure, it is affected by various harmful external and internal factors. Some illnesses are serious and require urgent treatment.
Who is most likely to have knee injuries?
The knees are formed by several bones connected by muscles, ligaments, tendons. There are also 5 synovial pouches - cavities surrounded by membranes designed to protect the joint. Between the joints of the bones are the interarticular cartilages - the menisci, which help the knee to move freely. Violation of the work of a part of the knee joint leads to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Especially often pain in the knee joint appears in people with flat feet. This is a pathology of the foot, which violates the shock-absorbing capabilities of the limbs. With age, increasing loads on the joints cause their destruction and the development of inflammation - a pain syndrome appears. Similar consequences have various types of deformation of the foot, leg.
There are several factors under the influence of which knee pain most often appears:
- overweight;
- Passive lifestyle;
- High sports loads;
- Diabetes;
- Vascular diseases;
- Elderly age;
- Knee operations and injuries;
- Work with increased load on the legs.
The causes and treatment of knee pain vary widely, as does the severity of the sensations. If the knee hurts a lot, the cause may be an injury or an advanced stage of osteoarthritis, a serious inflammatory process. Sometimes the symptom becomes permanent, even at rest, accompanied by swelling, redness of the skin and a flare-up. All these signs should alert a person and force him to visit a doctor.
Pain due to knee bruising
Among the traumatic causes of joint dysfunction, contusions are the most common. Why does the knee hurt if the symptoms were preceded by only a small bruise? Even a slight injury is accompanied by hemorrhage in the periarticular soft tissues, their swelling. As a result, the nerve roots suffer, pain appears.
In more severe cases, knee pain increases with flexion and extension of the leg, the person stops moving due to sharp sensations in the joint. On palpation, swelling of the leg can be noted, it is warm to the touch. How to treat such an injury? You should contact a traumatologist, get an x-ray, follow all recommendations and ensure peace of mind for your leg.
Often, traumatic hemarthrosis becomes the cause of pain in the knee joint after a banal bruise. This is a spillage of blood into the joint cavity, causing edema, swelling of the synovial membranes. As a result, the joint is filled with blood, inflammation begins in it. Without proper treatment, an injury can result in the development of chronic osteoarthritis, even at a young age.
Other types of knee injuries
If the leg at the knee hurts and the trauma contributes to these sensations, the causes may lie in various damage to the components of the joint. Here are the main ones:
- meniscopathy. It is a flattening or tearing of the meniscus. Especially often the injury is observed in professional athletes, in people involved in extreme sports, as well as in home injuries. A person feels that the knee is seriously ill, the nature of the sensations is stabbing, dagger, the joint loses mobility for a while.
- Ligament damage. A tear (sprain) of the ligaments occurs when the leg is twisted, after a jump, the limb is extended in an unnatural position. There is a sharp pain, the leg swells, the position of the joint changes, it becomes loose.
- Rupture of the cruciate ligament. As these ligaments are located within the joint, an injury often leads to bloodshed in the knee cavity. Just one puncture will help pump blood and make an accurate diagnosis.
Painful knee joint pain sometimes accompanies chronic patellar dislocations. Without treatment of an acute injury in many patients, the dislocation becomes chronic and relapses regularly. In children, this pathology causes an X-shaped curvature of the leg and leads to a serious violation of its function. Sometimes the pathology affects the knees on both legs.

Inflammatory knee diseases
The standard treatment for knee pain is often ineffective. In this case, not the joint itself, but the surrounding soft tissues may be affected. So tendinitis, or tendon inflammation, can be triggered by increased stress on the limb, past leg injuries, allergies, drug reactions, etc. The knee joint hurts with this disease, as a rule, during the day or at night, at night the pain subsides. In the acute phase, joint mobility is severely limited, the syndrome is persistent, not amenable to therapy with ointments, creams. Sharp sensations are also observed on palpation of the lateral part of the knee.
If the knees regularly ache, the symptom worsens after hypothermia, the cause may be synovitis - inflammation of the synovial membranes. An inflammatory exudate appears within the joint, which causes sensations of tearing and pain. The causes of the pathology are varied:
- autoimmune diseases;
- Metabolic diseases;
- Past injuries;
- Osteoarthritis.
Another "popular" disease where the knees hurt is bursitis. It occurs when the bursa (joint pouch) becomes inflamed. In addition to the pain syndrome, there is redness, swelling, increased sensitivity of the patella area. If you don't clarify in time how to treat bursitis, it almost always becomes chronic.
Neoplasms of the knee joint area
Malignant tumors of this location are rare, the pain syndrome is typical for them only in the very late stage. Most often, aching pain in the knee joint is inherent in benign formations:
- Baker's cyst. This tumor occurs under the knee, on its posterior surface. In appearance, the skin above the cyst is normal, not inflamed; in the folded form, swelling may not exist. In the standing position, a clearly defined, soft, elastic formation appears at the site of the cyst's location. Appears after a unilateral knee injury, suffered cartilage damage. Often, the cyst accompanies chronic synovitis, arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis. Large cysts cause not only knee pain but also a serious limitation of limb mobility. Due to the compression of blood vessels and nerves, other symptoms are coldness of the skin, pallor, chills and numbness.
- Meniscus cyst. It appears in the external or internal meniscus, when a cavity with fluid is located inside the cartilage. The knees, in this case, hurt after high loads or at the end of the day. Large cysts may be visible on the lateral side of the joint, while smaller cysts are only visible on ultrasound or x-rays.
A rare pathology is Hoff's disease - the transformation of fatty tissue in the joint, which becomes fibrous and causes joint dysfunction. Against the background of this pathology, osteoarthritis often develops, which causes pain in the knee joint. Causes - hormonal disorders, menopause in women.
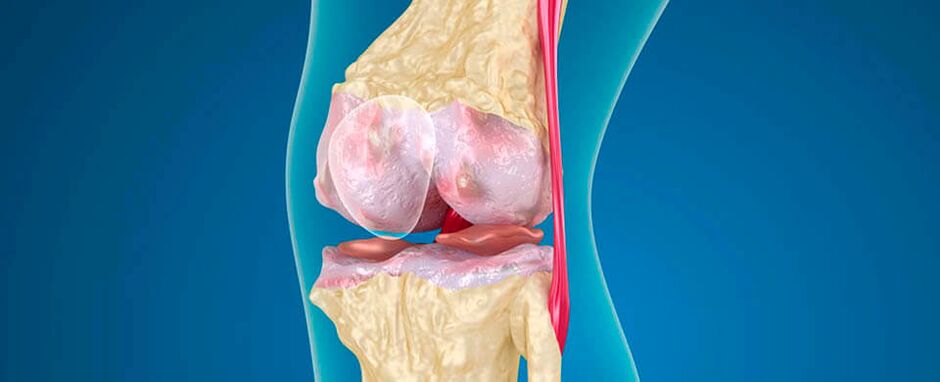
Infectious pathologies of the joint
Against the background of infection, the knee joint hurts sharply, providing rest does not cause relief. Even urogenital and intestinal infections can bring complications to the musculoskeletal system, resulting in reactive arthritis. Bacteria (salmonella, chlamydia, gonococci and others) penetrate the joint cavity of bones with blood flow, settle in tissues and cause inflammation. The tendons are also often inflamed, so the knee feels swollen and hot to the touch.
Tuberculosis is a serious disease. Mycobacterium tuberculosis multiplies in bone tissue, causing bone fusion, cartilage and soft tissue necrosis. Without emergency treatment, knee joints ache and collapse, and the process covers more and more areas. As a result, fistulas appear - cavities with pus, which can leak and cause damage to the entire organism.
An acute and urgent disease is osteomyelitis of the bone. What to do if the knees hurt and the process is accompanied by weakness, muscle pain, fever up to 40 degrees? If the pain in the knee is boring, bursting, and the tissues themselves are swollen, red, with blue, you should urgently call an ambulance and have an emergency operation. Otherwise, you could lose a leg or die.
Knee pain - causes of a degenerative nature
After age 50, a large number of people have knee pain. The prerequisites are the aging of the body, wear and tear of the joint apparatus and the development of the most common pathology - osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis). This leads to thinning, destruction of cartilage with a change in the shape of the bony heads. Most often, at an early stage of the pathology, the knee hurts on one side, after a few years the injury becomes bilateral. In the morning, leg stiffness worries but passes quickly. Increased sensations are possible after physical work, intensive sports, long walks.
In advanced stages, joint tissues collapse, osteophytes grow to the sides of the joint space. These are spikes made of bone tissue, which in severe cases break and cause unbearable pain. There are several degenerative pathologies, the symptoms of which will be similar to gonarthrosis:
- Osteochondropathy. It affects the articular surface of the bone, is associated with trauma, sports. Teenagers can develop for no apparent reason.
- Arthritis. It turns rheumatoid, psoriatic, gouty, causes chronic inflammation and joint destruction.
- Chondromatosis. The etiology is unclear. The disease causes the appearance of knots in the synovial membranes, which limit knee movement and cause pain.
Menopausal women often have knee pain due to osteoporosis - thinning of the bones, increasing their fragility. The disease is accompanied by leg cramps, pain in the spine, periodic fractures.

Other Prerequisites for Knee Pain
When the knees hurt, the etiology of the sensations can also lie in the defeat of the peripheral nervous system. Thus, sciatic nerve neuropathy against the background of damage to the lumbar vertebrae leads to various symptoms. A person's knees break, the thigh area hurts, the limb joints weaken, the skin sensitivity is disturbed. Leg reflexes also change.
Sometimes the entire knee joint hurts due to vascular disorders. Only in adolescence you should not worry too much - due to the rapid growth of the body, the vessels do not have time to supply blood to the bones. With age, the state of the joint normalizes - usually by the age of 18-20, the pain completely stops.
In old age, in the presence of atherosclerosis, the knees also tend to hurt, what to do in this case? Without normalizing fat metabolism, plaque will continue to build up inside the arteries. The vessels get clogged, stop feeding the joint as much as possible. Osteoarthritis develops, the pain becomes chronic. Unpleasant sensations in the knee region can also be caused by varicose veins, thrombophlebitis and vascular thrombosis.
How to make a diagnosis?
People's knees quite often hurt - how to treat the condition that arose can only be determined after an examination. Sharp, pulling pains in the knee are characteristic of a mass of pathologies, some of which are very dangerous. For diagnosis, you must contact a surgeon, orthopedist, neurologist, rheumatologist, traumatologist. He will carry out a survey, find out the exact symptoms of the disease, determine the accompanying signs. In addition, the doctor at the initial visit will perform a series of tests and physical exams to clarify the nature of the problem.
What to do when your knees hurt, what instrumental methods will help to identify the causes? Usually assigned:
- ultrasound;
- magnetic resonance;
- CT;
- X-ray.
The choice of the exact technique should be left to the physician. So, the ultrasound reflects well the changes in the leg with arthrosis, meniscus injury. The radiograph perfectly shows bone deformities, presence of osteophytes. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography provide complete information and are indispensable for complex diseases. In addition, the doctor will prescribe blood tests to exclude inflammation and rheumatism, if necessary, a biopsy of the joint will be done. With osteoporosis, densitometry is needed - it will show the density of bone tissue in a patient.

Knee pain treatment
If the pathology is traumatic in nature, then traumatologists are involved in the treatment, sometimes it is carried out in a hospital. Mild bruises disappear on their own in a few days, for quick resorption of the hematoma, it is advisable to apply absorbable ointments to the knee. With pain, it is necessary to rub ointments with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory components.
How to treat when the knee hurts with its inflammatory injury? In the acute phase of bursitis, synovitis, arthritis, the affected leg needs to rest, ice packs can be applied for 15 minutes during the first 3 days. Severe pain is relieved by injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, injections of anesthetics directly into the joint. To prevent chronic inflammation in the joint after the pain subsides, physical therapy and exercise therapy are prescribed.

When a person has knee pain due to gonarthrosis, what to do in this case? The main drugs for treatment are chondroprotectors and hyaluronic acid injections. These drugs are designed to restore nutrition to the joint cartilage, as a result, it stops breaking down. Also for knee rehabilitation should be assigned:
- vascular drugs;
- Physiotherapy;
- Fitness;
- Massage;
- Vitamin complexes.
Infectious joint diseases are an indication for the introduction of antibiotics into the joint cavities or oral administration of drugs. In some cases, it is necessary to have an operation, removing the tissues affected by the pus. Surgical intervention is also used to treat advanced forms of osteoarthritis with osteophyte growth. Sometimes, just replacing a joint with a prosthesis allows a person to maintain the ability to walk normally.



































